The Best Ways of Authentication

Current technology is always developing and also increases the risk of being hacked. In one of our previous articles, we already talked about hackers and the ways to protect your personal data. Nevertheless, the question remains relevant. In this article, we’ll talk about the ways of current authentication and try to understand what way is the most reliable. Good security can be difficult in theory but in practice, human behavior makes it even trickier. Let’s be honest, security best practices are hard enough to implement and almost impossible to enforce. However, you don’t have to go out of your way to get used to sophisticated new security procedures, but basic knowledge is essential for secure authentication.
Passwords
One of the most widespread and well-known methods of authentication are passwords. Passwords have been existing for a long time. However, it’s becoming more and more complicated to use password authentication as we have to create not one but a number of various passwords. An average person uses about 25 different websites and applications that require a password. To feel safe you need to create reliable passwords that should be long enough and consist of various numbers, letters, and characters. The problem is that it’s actually pretty hard to remember all these passwords. Trust us, even if your memory is good enough, it’ll be quite difficult for you to recall all your passwords.
In a data breach, such as the one that occurred at eBay (168 millions of users), passwords became the favorite targets of programmers. According to many security programs, websites can store passwords only in a “hashed” form (they’re cryptographically changed so that it’s impossible to read them directly but they can be easily recognized while logging in). All these precautions are made as hackers are capable of stealing a website’s database with all the passwords. Nowadays are being created many malware programs with the main goal to steal your passwords and personal information.
If your information is cryptographically transformed by the websites properly, you may not worry about your data. The process of reconstructing passwords is tough and time-consuming. Nevertheless, not all websites are so conscientious and that makes stealing passwords quite an easy task. So it’s not actually safe to use passwords or simple variations on every website. Hmmm… if it’s not safe to use passwords, what should we use? There are various kinds of authentication. Let’s look at the most spread ones.
Two-Factor Authentication
Despite all the passwords, there are many services that allow you to add a second level of security, through the use of two-factor authentication. It can either be a code generated on your device or sent to your phone. It’s also possible to generate such code on an external device.
At first glance, this type of authentication may seem much more reliable than simple passwords. Nevertheless, here are some pitfalls too. The problem is that the user could lose access to his SIM or a phone card or the process that is responsible for the code generating. Worst case scenario, you might even lose your device.
Captcha Test
CAPTCHAs are a type of of Turing test that we previously described in one of our articles about Artificial Intelligence. Its main goal is to make sure that you’re not a robot. Users are asked to perform some tasks that bots are not capable of doing. During such tests are used various images as while bots are capable of identifying an image by reading the source code, they won’t be able to understand what these images depict.
There’re different types of CAPTCHAS. One of the most common are the text CAPTCHAS where you need to look at random combinations of letters and numbers in the picture, determine it and finally enter the characters in the attached form. Some text CAPTCHAS could also be rendered as MP3 audio recordings as bots are only capable of determining the presence of the audio but not its content.
The other types of the CAPTCHA are the following:
- 3D Super CAPTCHAs — requires identifying an image rendered in 3D
- CAPTCHA “I’m not a robot” — requires a user to check a box
- Marketing CAPTCHAs — requires typing a particular word or phrase related to the sponsor brand
- Math CAPTCHAs — require a user to solve a simple mathematician task
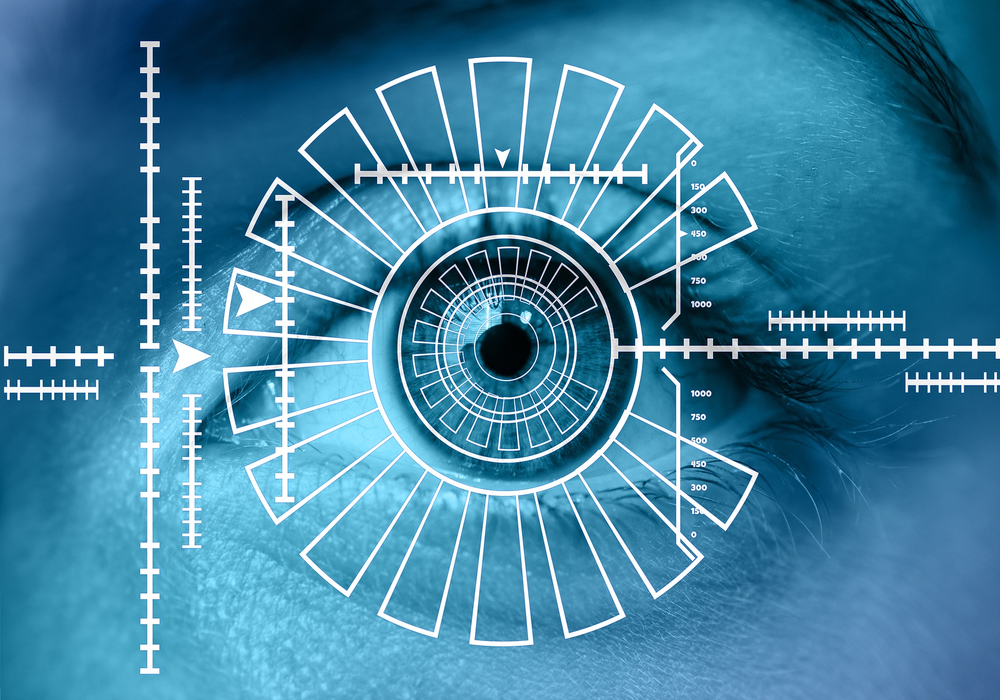
Biometric Authentication
This security process relies on the unique biological characteristics of a person to verify whether it’s true or not and that he’s who is says he’s. A user’s biometric data is captured and then stored in the database. One of the main advantages of biometric data is that you won’t be able to forget or lose it.
Various types of biometric authentication:
- Finger vein identification — this is the most common means of authentication that is used in the majority of digital devices
- Face identification — this technology is capable of scanning and identifying your face
- Voice identification — the technology relies on specific characteristics created by the shape of the speaker’s mouth and throat
- Fingerscanning — type of authentication resembles ink-and-paper fingerprinting process. This kind of authentication is also found as a Touch ID
- Iris recognition — the goal of this authentication method is to identify people based on unique patterns within the ring-shaped region that surround the pupil of the eye
What’s important is that biometric data can’t be cryptographically changed. In other words, that means that this data can’t be hashed. The thing is that all biometric data can never be the same. If we store biometric data cryptographically transformed that means that we won’t be able to compare it with other data. Even the slightest variations would change this hash.
Another disadvantage of biometric data, is that it’s quite difficult to use this data online. First off, it’s quite difficult to read biometric data remotely. While a device can verify the integrity of a fingerprint scanner and camera, an online service won’t be able to. In case we won’t find a way to securely store our biometric data, it always would be highly vulnerable to theft.
Authentication and Machine Learning
Imagine you’re going for a walk and notice your friend. There is an intricate process in your brain before you realize that you know this person. You need to take a lot more things into account than just a name or password. Human’s brain is much more complicated than any intricate technology or mechanism. We look not only at biometrical data, such as fingerprints, voice or face identification but also at human’s behaviour. Machines become more and more capable of observing and analyzing human behavior. It can significantly contribute to improving other authentications procedures. For instance, our computer would be able of recognizing the way we type our messages or passwords or even the way we talk on the phone. As a result, by learning the way we behave ourselves, our devices will be able to determine their true owner and in case of danger to shut down or erase themselves.
Public and Private Key-pairs
This kind of authentication is the main characteristic of asymmetric cryptography. It can be mostly found in such systems as Bitcoin, but public and private key-pairs might easily find a use in the authentications systems as well.
The user’s private key can be stored on the device and the public one can be uploaded and stored on a service’s servers. As a result, you’ll be able to use the same key-pair for various services.
The user wouldn’t need to transmit a password to log in but would create a signed message specifying details of the current login. It might be limited to some actions, such as access to certain folders or activities.
The Bottom Line
According to all the information above, and taking all the ways of authentication into consideration many researchers stick to the opinion that the most reliable way of current authentication is password. To identify a previous user without a password is really challenging and this process is costly and time consuming. The next biggest issue is to reset a password which is really easy to abuse with many services.
One of the main advantages of passwords is their simplicity in use and administer. If you’re convinced of their veracity, appropriate education provided, and a little care taken, passwords can become highly effective and provide adequate protection. Nevertheless, remember that passwords are kind a form of “what you know” security. On the one hand, they’re vulnerable to attack if used alone. On the other hand, they’re powerful when used in others forms of authentication with what you have (such as identification card) and what you’re (such as Finger vein identification, face/voice identification, finger-scanning).
Network administrators should create policies for site security, including password administration. Users, in their turn, must understand these policies. It’s extremely important to remember that with hundreds of thousands of computers on the Internet that each have hundreds or thousands of user accounts, a skilled hacker needs only a few successful entry points to cause significant damage.